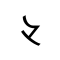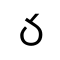Rma script
This article needs additional citations for verification. (April 2025) |
| Rma script Rrmea bapa | |
|---|---|
| Script type | |
| Creator | Wei Jiuqiao (Chinese: 魏久乔Category:Articles containing Chinese-language text) |
Period | 2017–present |
| Direction | Left to right, new line underneath |
| Languages | |
| Unicode | |
| proposed[1] (U+16140 - U+1617F) | |

The Rma script (Northern Qiang: Rrmea bapaCategory:Articles containing Northern Qiang-language text) is an alphabet with some abugida-like features[2] devised for the Qiang language, spoken in Sichuan Province in the southwest of China. It was finalized in 2017 by scholar Wei Jiuqiao.[3]
The script fits the phonology of the standardized language of the Northern Qiang variety of Qugu, officially written with the Roman script using the Qiang Phonetic Alphabet Scheme. Whereas Northern Qiang varieties have length contrasts, Southern Qiang varieties have phonemic tone contrasts; thus a version with tonal diacritics has also been produced, and has been used for the Southern Qiang variety of Luobuzhai (Chinese: Category:Articles containing simplified Chinese-language text萝卜寨; pinyin: Luóbozhài) in Wenchuan County.[2] It has gained substantial recognition among the Qiang people, and various books have been published in it.[3]
In 2022, a preliminary proposal was made to encode this system in the Universal Character Set of Unicode.[1]
Consonants
The ordering of the consonants proceeds from labial stops to velar stops and then to the affricates; in this regard, its ordering is similar to the Bopomofo system for Standard Chinese.
In contrast to true abugidas, the consonant glyphs do not have inherent vowels attached, and thus is closer to a true alphabet.
Vowels
The Rma script has abugida-like features in its vowels, with its use of vowel diacritics around the consonant glyphs, and a zero consonant character.
Note the use of the same glyph for vowel length marking and the glottal stop, in Northern Qiang: agveiCategory:Articles containing Northern Qiang-language text. It is also the vowel carrier glyph.[2]
Punctuation
The Rma script has its own punctuation,[2][3] including a special ligature for the Qiang people.[3] It was from this sign that the writing system was devised.[2]
Tones
This section is empty. You can help by adding to it. (November 2024) |
References
- 1 2 Chan, Eiso; Wei, Jiuqiao; Sims, Nathaniel (6 June 2022). "Preliminary proposal to encode Rma script to UCS" (PDF). Unicode. Universal Multiple-Octet Coded Character Set. Retrieved 13 November 2024.
- 1 2 3 4 5 "Qiang Script". weijiuqiao.github.io. Retrieved 13 November 2024.
- 1 2 3 4 "Qiang / Rma Script". omniglot.com. Retrieved 13 November 2024.